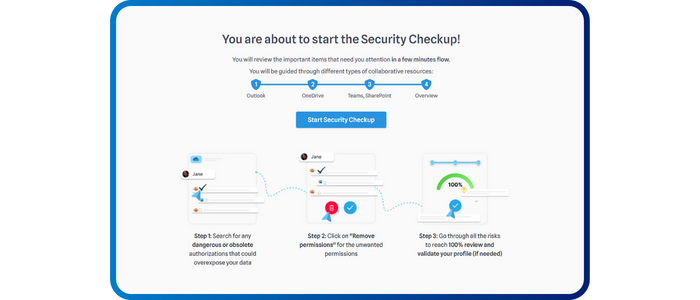
Security CheckUp: Simplifying risk review in M365
Lire l'article[NEW] MYDATAMANAGEMENT TO CLEAN UP YOUR OBSOLETE, UNUSED AND VOLUMINOUS DATA
Solutions
Effective response to six major challenges in data security
#1 user-interacting platform for detection
Discover the platform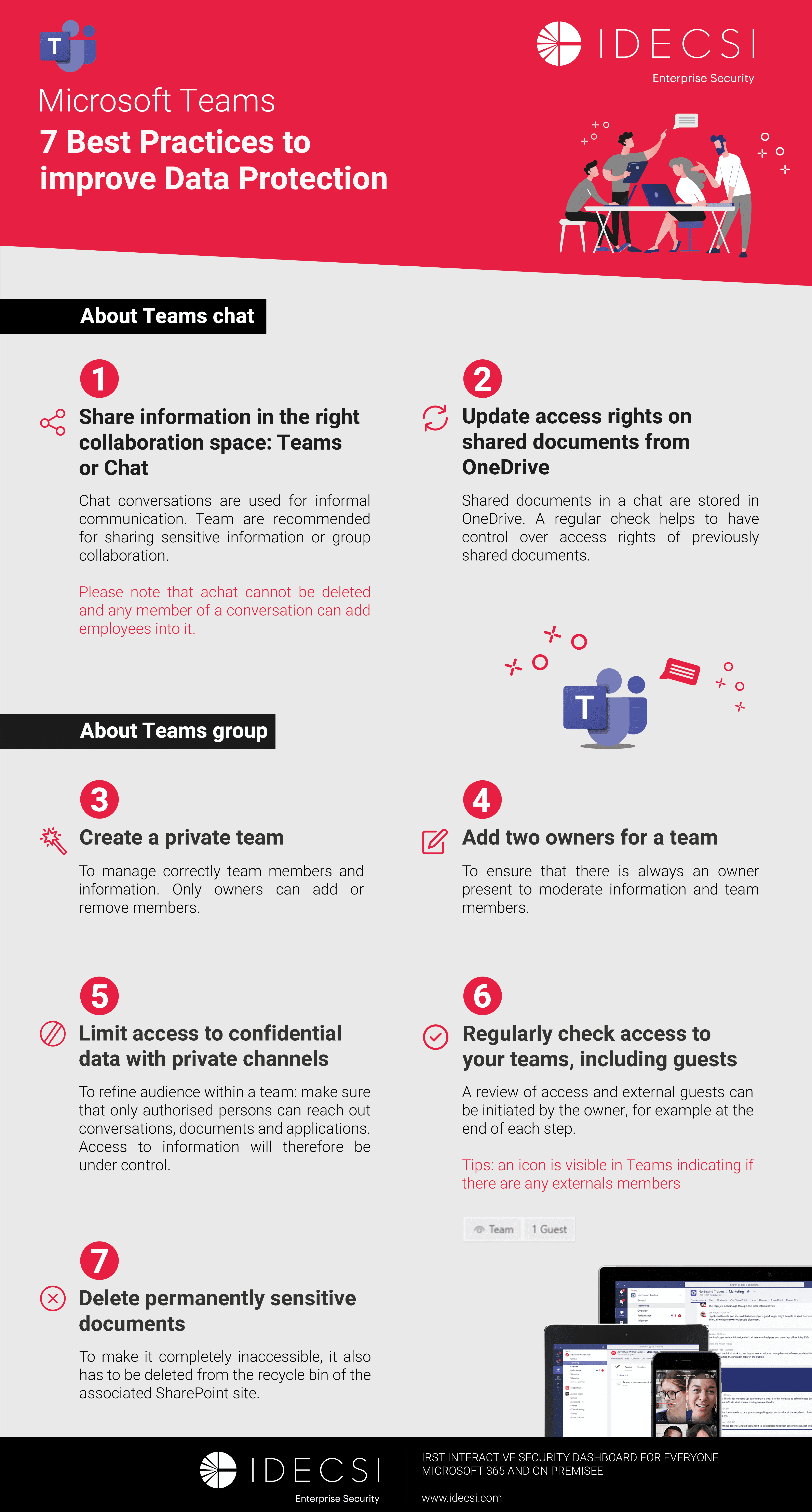
Best practices to improve Microsoft Teams security
Download the infographicOur resources
Check out our useful resources for improving data protection
Microsoft 365
03 February 2026
Copilot represents the biggest change in enterprise productivity since Microsoft invented Office. But it poses a real challenge for IT security and governance.
Imagine a tool capable of scanning, analyzing, and synthesizing thousands of your company's data points in seconds.
Is it powerful? Yes.
Is it dangerous? Absolutely, if your access controls aren't locked down and properly managed.
In 2026, adopting generative AI is no longer an option—it's a competitive imperative. Yet, "79% of IT decision-makers cite data privacy as a major concern," according to Gartner.
Scaling Microsoft Copilot for enterprises is a real challenge. This guide is designed for CIOs, CISOs, and IT decision-makers.
We'll explore what Copilot is, how it works, its real-world use cases (beyond the marketing), and most importantly: how to deploy it without exposing your company's secrets.
What is Microsoft 365 Copilot?
Microsoft Copilot isn't just "ChatGPT in Word." It's a sophisticated orchestration engine.
Simple definition:
Microsoft 365 Copilot is an artificial intelligence integrated directly into your daily applications (Teams, Outlook, Excel, PowerPoint). Unlike public AI tools, it combines the power of LLMs (Large Language Models) with your enterprise data (files, chats, emails) via Microsoft Graph, all within your security perimeter.
Fonctionnalité |
ChatGPT / Claude (Public) |
Microsoft 365 Copilot (Enterprise) |
|
Data Source |
Internet (public) |
Your tenant data (private) + Web |
|
Privacy |
Data used for training (often) |
Zero training on your data |
|
Rights Compliance |
None (universal access) |
Strict respect of ACLs / Permissions |
|
Integration |
Manual copy-paste |
Native in Office apps |
Microsoft's offering has stabilized around three pillars. Don't confuse the free tool with the enterprise platform.
Now included in most Microsoft 365 Business and Enterprise licenses. It offers Commercial Data Protection, but remains limited: it doesn't access your internal data (Graph) and doesn't integrate deeply into Apps. It's a "secure ChatGPT."
This version is an add-on requiring a base license (E3, E5, Business Premium, etc). his is the version we'll discuss today. It provides:
A completely separate product, designed for SOC (Security Operations Center) teams. It's not billed per user, but based on compute power consumption (Security Compute Units), to analyze incidents in real-time.
However, Microsoft announced in early 2026 that the SCU model will also be included in E5 licenses.
Good to know: Don't confuse Microsoft 365 Copilot (the ready-to-use assistant) with Copilot Studio (the low-code platform). Use Studio if you need to connect Copilot to external data (Salesforce, SAP, Jira) or create custom agents.
Chat is ephemeral, work is persistent. Copilot Pages transforms your AI conversations into living, multiplayer documents.
Instead of losing the result of a prompt in a discussion thread, you save it in a "Page." Your entire team can then edit, enrich, and correct the AI-generated content in real-time. It's the modern enterprise's new whiteboard.
Agents represent the major evolution of Microsoft 365 Copilot in 2026. Where classic Copilot answers your questions, agents act for you.
According to Microsoft, "agents use AI to automate and execute business processes, working alongside or on behalf of a person, team, or organization. They range from simple conversational agents to fully autonomous agents."
The fundamental difference: An agent can monitor a mailbox 24/7, automatically analyze incoming requests, draft contextualized responses, and update your business systems (CRM, ITSM, HRIS) without constant human intervention.
Microsoft distinguishes two types of agents:
Two creation methods:
Copilot Studio Lite (simple): Interface accessible directly in Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat. No technical skills required. Ideal for quickly creating a conversational agent that responds based on your SharePoint documents.
Copilot Studio (advanced): Complete low-code/no-code platform (Power Platform) to connect external systems, create automated workflows (Power Automate), and manage secure agent identities (Entra Agent IDs).
Examples of Microsoft agents in production:
Typical business use case: An agent "Customer Support" monitors a generic mailbox, analyzes incoming message sentiment, drafts a response respecting your brand tone, and automatically updates the ticket in your CRM. This agent requires Copilot Studio with Power Platform connectors (Graph API, CRM) and a dedicated Entra Agent ID identity.
For security purposes, you need to understand its architecture.
Microsoft 365 Copilot follows a strict security model to protect user data. It uses Microsoft Graph to access organizational information from the user's tenant, such as documents, emails, and calendars.
The process occurs in 3 critical stages:

(Note: Visualize a flow where your data never leaves your tenant's compliance bubble)
Critical security point: Your data is NOT used to train Microsoft's AI models. Tenant isolation is contractual.
Here's what your teams will actually do (beyond the hype):
|
Application |
Key features |
|
|
Teams |
Meeting summaries, action items, catch-up on missed conversations |
|
|
Outlook |
Priority sorting, contextual response drafting, long thread synthesis |
|
|
Word |
First drafts, summaries, tone changes, table creation |
|
|
Excel |
Data analysis, charts, cleaning, formulas |
|
|
PowerPoint |
Slide creation from Word documents, auto design, speaker notes |
The magic relies on the Semantic Index for Copilot. It's a sophisticated map of your data. It doesn't just search for keywords ("Project Alpha"), but for concepts ("The meeting where we decided on the Alpha budget").
It applies Security Trimming in real-time: Copilot only "sees" what the user has permission to see. If the user doesn't have access to the Salaries_2026.xlsx file, Copilot will act as if it doesn't exist.
The productivity promise offered by Microsoft 365 Copilot has quickly won over numerous companies worldwide. Today, nearly 70% of Fortune 500 companies use it! According to an IDC study, 75% of companies that adopted Microsoft 365 Copilot in 2024 generate an average return on investment of $3.70 for every dollar invested. For some executives, this return could even reach $10.*
Here's how our clients use Copilot today.
Situation: Quarterly Board preparation.
Prompt: "Summarize Q3 financial results from Finance Excel files, add highlights from strategic projects mentioned in my emails with the Executive Committee, and identify major risks."
Result: A consolidated multi-source view in 5 minutes instead of 4 hours of compilation.
Situation: Creating a job description.
Prompt: "Create a job posting for a Senior DevOps. Use the inclusive tone from our diversity charter [Link], and base it on the technical skills from Thomas's job description [Profile link]."
Gain: Employer brand consistency and massive time savings.
Situation: Technical documentation (developers' bane).
Prompt: "Generate technical API documentation from this source code segment. Explain the input and output parameters."
Gain: Reduction of technical debt.
Situation: Critical client meeting preparation.
Prompt: "Synthesize the entire 'Client Name' client history: latest emails, ongoing CRM deals, and friction points mentioned in Teams transcriptions."
Result: An ultra-prepared salesperson who arrives at the meeting with complete context.
The entry into force of the European AI Act has redefined the rules of the game. While Microsoft (the "Provider") bears the burden of the technological model's compliance, your company, as a "Deployer," has specific legal responsibilities regarding the use of generative AI.
Here are the 4 imperatives to respect for your 2026 deployment:
Your employees and third parties must know when they're interacting with AI or consuming AI-generated content.
AI adoption requires "accountability." You cannot deploy the tool without a formal framework.
You cannot simply "turn on" Copilot. The law requires that people responsible for using or supervising AI systems have the necessary skills.
The AI Act indirectly reinforces GDPR requirements.
To ensure compliance, you must ensure that data injected into the system (via Grounding) is legitimate. Strict access rights governance prevents Copilot from processing personal or confidential data accessible by mistake (oversharing), which would constitute a double violation.
Be careful with specific use cases. If you use Copilot for sensitive tasks like recruitment (CV sorting), employee performance evaluation, or access to essential services, your system may fall into the "High-Risk AI" category.
In this case, obligations explode: fundamental rights impact assessment, mandatory strict human oversight, and registration with competent authorities are required.
Copilot is powerful, but this power reveals your existing flaws. As we often say at IDECSI: "Deploying Copilot without governance is like turning every forgotten permission error into a potential overexposure."
This is the absolute danger. Copilot accesses everything the user can see.
The problem? In most companies, users have access to far more data than they think (accidentally "Public" files, open Teams groups, "Everyone" sharing links).
Catastrophic scenario:
An intern asks: "How much does the marketing director earn?"
If the salary Excel file is stored on a misconfigured SharePoint site (access "Authenticated Users"), Copilot will give the answer, the exact amount, and the source. It didn't hack the system, it just used existing rights.
For more information, discover our article on the 6 major risks of Copilot deployment.
Microsoft recommends 4 to 8 weeks of preparation. Don't skip this step.
It's crucial to have as complete a vision as possible of your tenant before deploying Copilot in your organization. Without this visibility, certain risks could escape you!Les 5 piliers de la préparation.
You must map your sensitive data, the people who handle it, and identify over-permissions.
This is the time to reduce attack surface and costs.
Gain: Considerable reduction in hallucination, overexposure, and leakage risks, plus storage cost savings.
Configure your DLP (Data Loss Prevention) policies to be "Copilot-aware". Define an acceptable AI usage charter.
Copilot doesn't replace humans, it augments them. But you need to know how to talk to it. Train your "Champions" in advanced prompting.
Start with a test group of 20 to 50 users. Measure adoption and adjust before general deployment.
For more information, discover how to prepare your Microsoft Tenant for Copilot's arrival.
To sleep soundly with an AI scanning your servers 24/7, the "we'll see later" approach is dangerous. Your data governance in Copilot must rest on a solid, interconnected triangle maintained in real-time.
This is your AI's fuel. If the fuel is polluted, the engine stalls (or explodes).
This is where 80% of cyberattacks start (via compromised credentials)
(Source : CrowdStrike Global Threat Report)
Microsoft's security model is complex: permission inheritance, broken sharing links, nested groups, guest access...
Principle of Least Privilege: A user should only have access to data strictly necessary for their mission.
Hunting "Toxic Permissions":
This is where IDECSI intervenes.
Microsoft's native tools are often too technical for a quick overview. IDECSI offers you an intuitive rights review tool: immediate and simplified visibility on who actually accesses what and concrete remediation actions.
We automate rights reviews by involving data owners (via internal email campaigns), as they're the only ones who know if access is legitimate. Supervised by administrators, these campaigns can also undergo mass remediation to remove residual problematic access and non-compliant shares.
Once the tool is deployed, you can't close your eyes.
Expert advice: Don't try to lock everything down manually. It's impossible given the volume. Automate monitoring of pillar 2 (Access) to ensure pillar 1 (Data) remains protected.
For more information, discover our 5 tips to secure data access from Copilot.
The advent of autonomous agents marks a rupture in cybersecurity. Until now, we've secured human identities. Now, you must secure non-human identities capable of executing complex action chains (read, analyze, write, send) at machine speed.
This new automation layer requires specific governance, beyond simple file permissions.
Microsoft anticipated this need by structuring agent identity. Each agent created (via Copilot Studio or by third-party publishers) now has its own identity registered in Microsoft Entra ID.
This is where Agent 365 comes in. It's not just a dashboard, but the nerve center for IT and Security teams. It allows you to:
For more information, discover our article on Microsoft's Agent 365.
If Agent 365 provides the technical tooling, real security rests on your operational strategy. Here are the four essential pillars for deploying agentic AI without losing control.
Don't trust an agent "by default" simply because it's internal.
The issue: An agent shouldn't blindly inherit all rights from the user who launched it (privilege escalation risk).
Best practice: Apply strict least privilege principle. An agent dedicated to "Meeting Summary" should have read-only access to Teams and Outlook, and strict prohibition of access to CRM or financial folders. Segment rights by "capability" and not by user profile.
Total automation is a risk for critical processes.
The issue: Prevent an AI hallucination from triggering an irreversible action (erroneous transfer, mass email sending, data deletion).
Best practice: Integrate mandatory "checkpoints" for sensitive actions. The agent prepares the work (draft, calculation), but the human validates final execution.
Note: To avoid killing productivity, target these validations. Email archiving can be automatic; sending a client contract must remain validated.
A poorly designed agent is a dormant vulnerability.
The issue: Ensure agents comply with company rules even before deployment.
Best practice:
The ease of agent creation (Low-code / No-code) is double-edged.
The issue: Your employees will create their own agents to make their lives easier, often without awareness of risks (e.g., an agent connected to a personal Drive to "save" professional documents). This is Shadow AI.
Best practice: Don't block innovation, frame it. Form "Citizen Developers" on data leakage risks and implement a rapid certification process for agents created by business units. Transform Shadow AI into "Managed AI".
Don't let security slow your innovation—master the risks.
At IDECSI, we are experts in M365 environment protection and governance. We collect and analyze millions of metadata daily for CAC40 companies and mid-sized enterprises.
Through a turnkey system, IDECSI allows you to identify and eliminate risks in your M365 tenant to deploy AI on a secure and up-to-date environment.
Our "DETOX for M365" offer:
Average result: 45% reduction in risk surface from the first month, IFOP study
Discover how TotalEnergies and Rocher Group successfully secured their data governance with IDECSI
Ready to Secure Your AI?
Microsoft 365 Copilot is an inevitable revolution in enterprise productivity. Those who adopt it gain a major productivity advantage. Those who ignore it fall behind.
But remember: speed without control leads to accidents. To fully exploit this tool's potential while controlling risks, it's essential to adopt a proactive approach to data management (lifecycle) and access.
Thus, rigorous preparation of your tenant (cleanup, permissions, governance) is the only way to guarantee positive ROI without sacrificing your security and protecting the company's strategic information.
Don't wait to face the risks—take back control of your data!
Want to go further? Discover how to optimize your M365 storage costs in our next article.
Recent articles
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive new contents every month
Our articles
These articles may
interest you