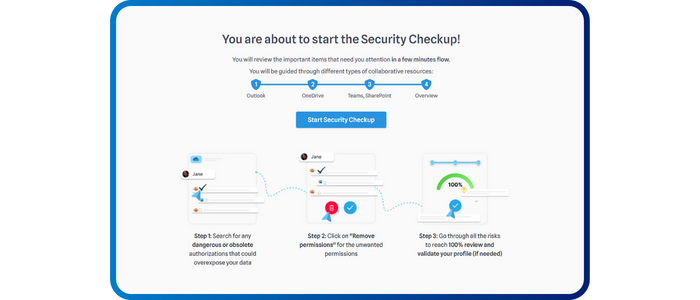
Security CheckUp: Simplifying risk review in M365
Lire l'article[NEW] MYDATAMANAGEMENT TO CLEAN UP YOUR OBSOLETE, UNUSED AND VOLUMINOUS DATA
Solutions
Effective response to six major challenges in data security
#1 user-interacting platform for detection
Discover the platform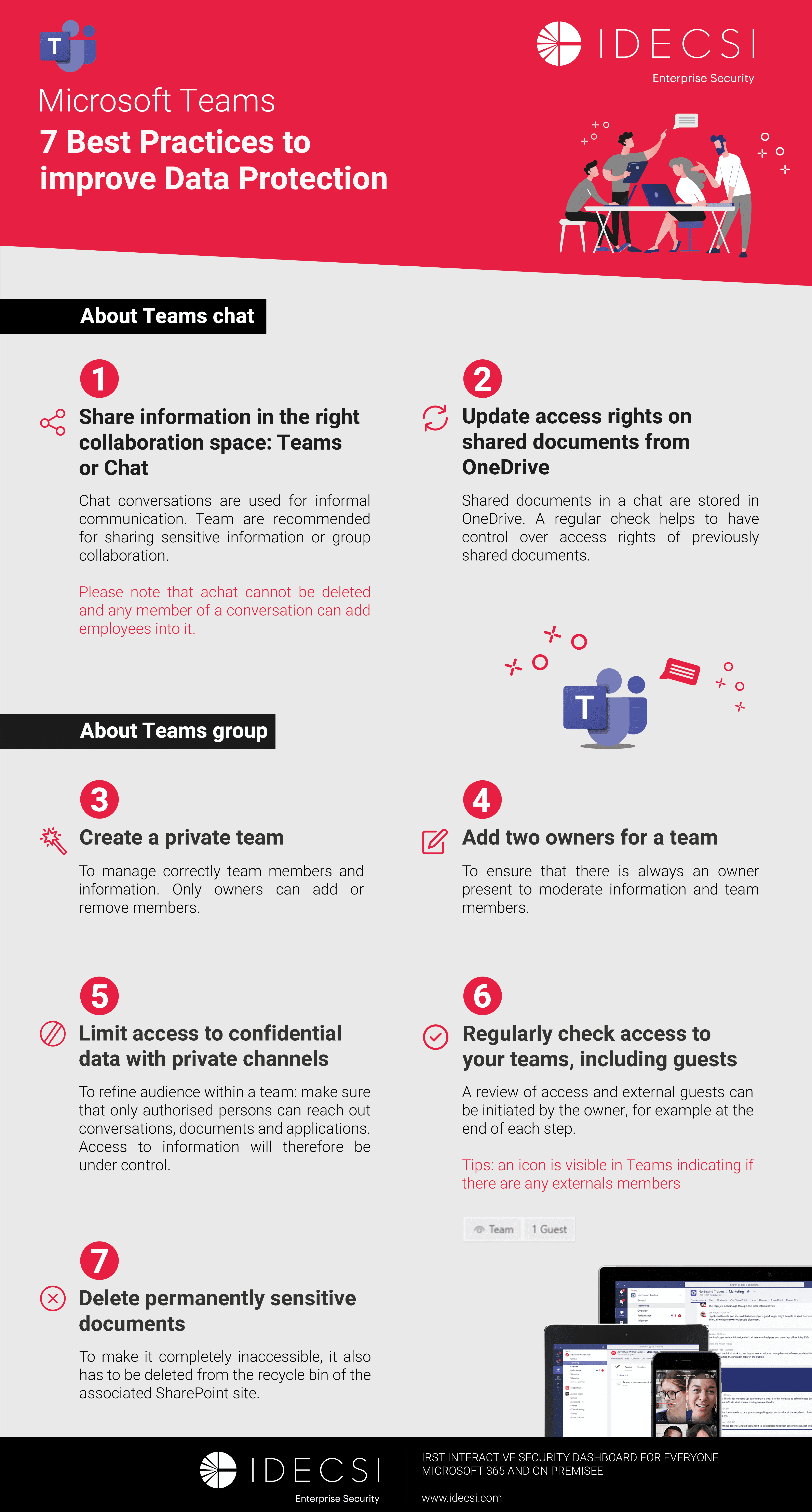
Best practices to improve Microsoft Teams security
Download the infographicOur resources
Check out our useful resources for improving data protection
Microsoft 365
13 October 2021

Microsoft, with its Microsoft 365 suite (formerly Office 365), dominates the collaboration tools market with 300 million licenses and over 50 million subscribers.
Large companies, small and medium-sized enterprises and even smaller companies have already deployed these solutions to increase the productivity and collaboration of their teams. At the same time, solutions to secure data on Microsoft are essential.
Microsoft 365 solutions offer unprecedented flexibility in information sharing and collaboration, allowing employees to connect to their work environment on a variety of devices and from any location.
However, this flexibility to access documents, data and other company information via SharePoint, OneDrive, Exchange, creates many problems and opportunities for highly targeted cyber-attacks on the information system.
That’s why data protection is an important issue, and companies have a vested interest in covering this topic.
In this article, we look at the risks and the means provided by Microsoft to secure and manage data without slowing down the use of the tools.
Microsoft has evolved its Office 365 offering, particularly in terms of pricing and features, and continues to offer cloud services to help businesses become more productive.
Microsoft 365 is a complete offer integrating different building blocks to improve collaborative work and data management.
The different tools or services are divided into different usage areas:
The first and best known, Microsoft Exchange, integrates Microsoft Exchange Server and Microsoft Outlook. It is an email service and email operating system, available on-premise or in the cloud.
Yammer is an enterprise social network that facilitates communication between groups of employees: knowledge sharing, success, top-down communication, community creation, and more.
Microsoft Teams, which is becoming the core tool of the suite, has more than 270 Million monthly active users worldwide in 2022 and +330,000 companies use Teams globally.
Teams is a communication and collaboration platform that facilitates exchanges and sharing, as well as the organization of remote meetings. The tool is composed of 3 parts: chat, meeting, and the collaborative groups that are the teams themselves.
OneDrive is a tool for individual storage and occasional sharing using cloud technology.
SharePoint allows you to create websites, intranets and document storage centers. It facilitates the storage, organization, sharing and consultation of information. SharePoint is available on-premise but also in the cloud with SharePoint Online.
Microsoft Power Platform is a set of code-free cloud development solutions. The three main tools are:
Formerly Microsoft Flow, Power Automate allows you to create and automate tasks and processes to facilitate the work of your employees.
This is a business application development service. It is the studio for creating applications with connectors between Microsoft solutions.
Power BI is a business analysis service from Microsoft. It aims to provide interactive visualizations and business intelligence capabilities with an interface simple enough for end users to create their own reports and dashboards.
Active Directory is the directory behind all these tools that allows IT and administrators to identify, authenticate and manage data, applications and users on the company’s internal network.
Administrators benefit from centralized management of users and access, roles and privileges, and centralized control of user configuration. Proper implementation of Azure Active Directory security is essential to protect the enterprise from unauthorized access.
The deployment of the Microsoft 365 suite generates profound changes for IT teams and users with regard to data security. What are the major challenges?
By migrating to the cloud, IT managers open up their information systems and delegate some of the data management to users, such as information sharing. Until a few years ago on file servers (on-premise) only a few directories facilitated the sharing of files internally. Today with the acceleration of the cloud and services like SharePoint online, users can easily share information without going through special permissions issued by IT teams.
This requires a new model of data governance on Microsoft 365 where the workplace, infrastructure and security teams must work together.
This migration also impacts identity management, especially with the freedom of internal/external collaboration.
It is essential to define a framework and develop the identity management strategy, the levels of authorizations granted (administrator, internal, guests) and the associated security measures (authentication, guest life cycle).
Security teams have less visibility into what is happening in the Microsoft 365 environment.
Once a base has been defined, the challenge is to master the new uses of Microsoft 365 collaboration tools to ensure data security and integrity.
Today, there is a paradigm shift, users have become the administrators of their own shares. Since data management is in the hands of the users, it is important to define rules around usage to clarify what the user can do and when.
A lack of security and awareness can lead to human error and potentially to a data leak.
Support in governance and access review is an issue that concerns both the workplace and security teams.
Moreover, monitoring does not stop after adoption of the software; the Microsoft 365 tools and the Digital Workplace trends evolve, and therefore so do their uses, opportunities and threats.
Discover the 12 best practices for improving security and collaborative uses of Microsoft 365.
One of the challenges companies are facing is the inflation of access and sharing and the exponential increase in the use of collaboration tools (Microsoft Teams, SharePoint Online). The volume of access logs and configuration objects to be analyzed is colossal. How can points of vulnerability and compromises in the IS be quickly identified?
The last issue is therefore around the implementation of security measures and tools to process this information and optimize the SOC workload.
This will involve the implementation of security tools on data protection, Microsoft 365 data auditing, detection, data monitoring and alerting.
40% of companies had one or more of their employees’ Office 365 accounts hacked during 2018. – Cyren and Osterman research study
The security risks of Microsoft 365 collaboration tools are both internal and external. CLUSIF has published a risk map on Office 365.
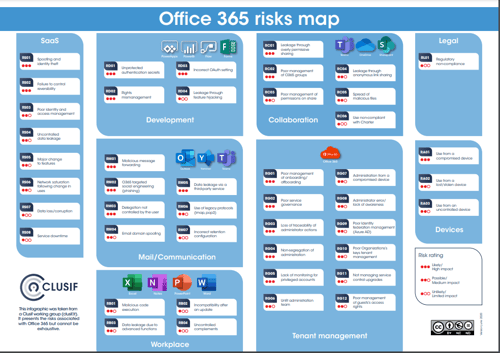
There are 3 levels of vigilance on Microsoft 365:
At the enterprise level, data security risks can occur with poor management of the Microsoft tenant.
A change in objects or configuration settings can impact the security rules in place or specific policies for sensitive data such as Microsoft Purview (MIP) labeling. Moreover, sensitive data is a strategic security point, it is necessary to be able to identify them and know where they are.
Privileged or administrator accounts, if compromised, can have serious security consequences. You must be able to initiate a security audit with a review of privileged accounts and monitor configuration changes.
At a business-wide level, we also see the issue of identity management. Indeed, bad invite management can cause problems of data leakage or legal problems (compliance). To limit the risks, administrators will have to work on the guest user lifecycle, the limitation of permissions, conditional access control, and awareness.
Each tool in the Microsoft environment has its own specificities that must be known and taken into account to ensure the best security settings.
On email/communication tools, Office 365 phishing is a common and one of the most effective attacks. The main risk lies in accessing sensitive data or access to administrator accounts.
Regarding collaboration tools, we will mainly talk about risks of leakage through overly permissive link sharing or poor management of permissions or even poor management of groups.
Find the 5 key points to know about Microsoft Teams security.
80% of CISOs surveyed identified employee sharing as a major risk to corporate data – CESIN, Barometer 2021
The impact of these human errors can sometimes be serious, even irremediable, and lead to major risks on data security, especially on the most strategic data.
The multiplication of link sharing methods means that a configuration error is always possible. The challenge is to reduce the risk related to shared data. This error can be caused by the user.
- Leakage via overly permissive sharing or over-sharing on SharePoint
- Poor group management
- Poor permissions management
- Leakage via anonymous link sharing
- Poor management of guest permissions
- Inbox rule in email (Outlook, Exchange)
- Uncontrolled delegation
How does IDECSI for M365 analyze suspicious activity and detect compromises?
To protect the Microsoft 365 suite, the American company integrates in its offer solutions for the security of data, employees and IT infrastructure.
Microsoft offers cloud coverage on core issues related in particular to identity protection and access management, protection and control of sensitive data and risk management.
Microsoft Azure Active Directory provides unified identity and access management for the cloud: identity lifecycle governance, access lifecycle governance (conditional access, Multi-factor authentication – MFA) and secure privileged access for administration.
In order to classify and protect sensitive data, Microsoft has developed a solution called Microsoft Purview Information Protection (formerly Microsoft Information Protection). This tool focuses on identifying and protecting sensitive data on files, groups and emails in the Microsoft 365 suite. In the Premium versions of Purview, the main functionality is the scanner. It allows you to automatically identify and encrypt sensitive data, and to track and control access to documents.
Risk management will involve threat detection, verification and remediation. The Microsoft Purview tool will help detect compromises and identify threats, and eDiscovery will reduce and verify the volume of data to be processed in order to send the right alerts to a SIEM.
The accessibility of these tools depends on the license levels. The licenses chosen will change the user experience and the security levels granted.
The highest is Microsoft 365 E5 which offers advanced security and analysis tools (Power BI pro). In general, companies only take on the Microsoft E5 license for VIPs or administrators because the cost is high.
IDECSI completes Microsoft’s offering to strengthen data security in cloud and on-premise environments.
Microsoft and IDECSI teams have been working on a mapping of the key security features of Microsoft 365. This document gives companies a better visibility on the construction of a global and optimized system. With the example of many use cases, it presents the relevance and the advantages of linking IDECSI with Microsoft.
Expert on Microsoft 365, the IDECSI monitoring platform collects multiple data sources from the Microsoft tenant to distinguish:
It covers all users and cloud and on-premise resources for advanced Microsoft 365 data protection with 5 key features:
Aware that employees have more and more power over the management of their data, IDECSI stands out from the crowd due to its connection with users. They can govern their data.
IDECSI increases the power of the company as a whole to improve efficiency and ROI when dealing with cybersecurity issues.
Recent articles
Subscribe to our newsletter and receive new contents every month
Our articles
These articles may
interest you